OIDC#
OIDCIt is a new authentication authorization agreement based on OAUTH2 and Openid integration
Four authorization modes#
The client must be authorized by the user(authorization grant),Only to get token(access token)。rfc 6749 Definition of four authorization methods。
- Authorization code mode(authorization code)
- Simplified mode(implicit)
- Password(password)
- Client mode(client credentials)
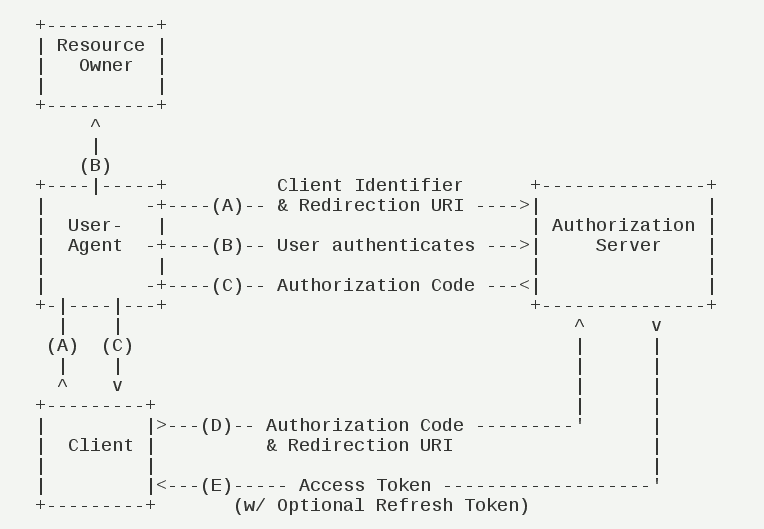
Authorization code mode(authorization code)#
Authorization code mode(authorization code)It is the most complete function、The strictest process、The most authorized mode of use。It is characterized by the background server of the client,and"service provider"The authentication server interacts。 Since this is a process -based process,The client must be capable and resource owner's USER-agent(Usually web browser)Interact,And have the ability to receive the redirection request from the authorized server。
Its steps are as follows:
(A)User access client,The latter will guide the former -oriented authentication server (ARKID)。
(B)Users choose whether to give client authorization。
(C)Suppose users authorize,Certification server (ARKID) specifies the user to the client in advance"Reset to URI"(redirection URI),At the same time, an authorization code is attached。
(D)The client receives the authorization code,Earlier"Reset to URI",Apply to the certification server (ARKID)。This step is done on the server of the client's background,No visible to users。
(E)Authentication server (ARKID) checks the authorization code and redirect to the URI,After confirmation,Send access to the client(access token)And update token(refresh token)。
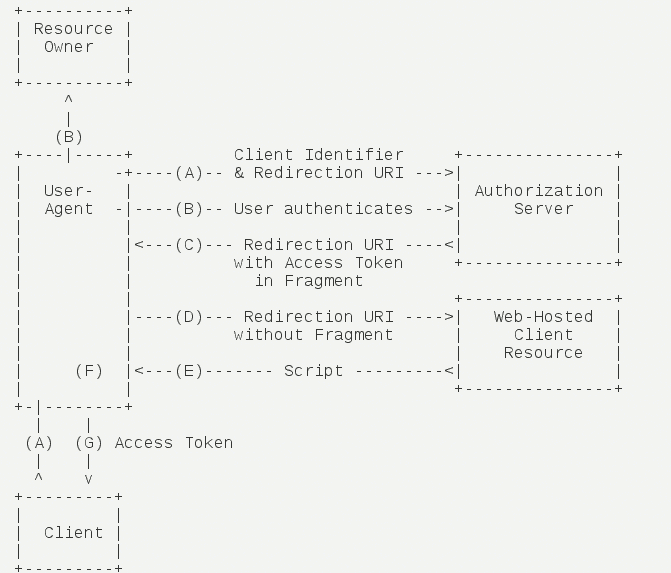
Simplified mode(implicit)#
Simplified mode(implicit grant type)Server without third -party applications,Apply directly to the certification server to apply to the certification server in the browser,Skip"Authorization code"This step,。All steps are completed in the browser,The token is visible to the visitors。
Its steps are as follows:
(A)The client will guide the user -oriented authentication server (ARKID)。
(B)The user decides whether to authorize the client。
(C)Suppose users authorize,Certification server (ARKID) specifies the user -oriented client"Reset to URI",And in the Hash part of the URI, the access token is included。
(D)The browser sends a request to the resource server,It does not include the hash value received in the previous step。
(E)Resource server returns a web page,The code contains can get the token in the hash value。
(F)The browser executes the script obtained in the previous step,Extract。
(G)The browser sends the token to the client。
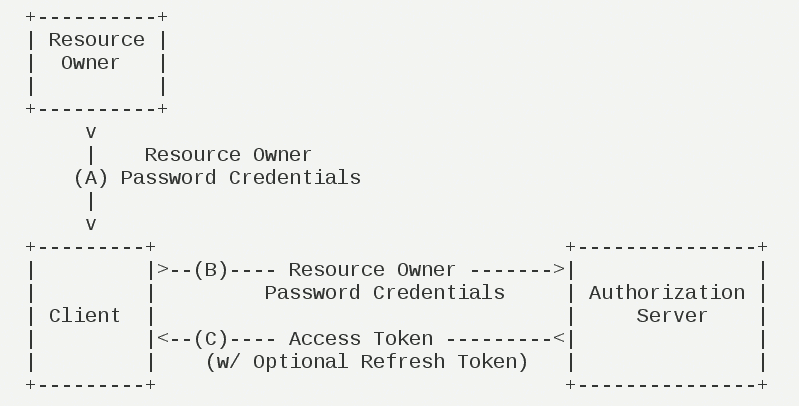
Password(password)#
Password(Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant)middle,Users provide their own username and password to the client。Use this information on the client,Towards"Service provider"Be authorized。 In this mode,Users must give their passwords to the client,But the client must not store the password。Risk,Therefore, it is only applicable to other authorization methods,And it must be a highly trusted application of users。
Its steps are as follows:
(A)Users provide user names and passwords to the client。
(B)The client sends the username and password to the certification server,Ask the latter to token。
(C)Authentic server (ARKID) confirmed that it is correct,Provide access to the client。
Client mode(client credentials)#
Client mode(Client Credentials Grant)Refers to the client in its own name,Instead of the name of the user,Towards"Service provider (ARKID)"Certify。Strictly speaking,The client mode does not belong to the problem that the OAUTH framework is to solve。In this mode,Users register directly to the client,The client is in its own name"Service provider (ARKID)"Provide services。
Its steps are as follows:
(A)The client conducts identity authentication to the certification server,And ask a access token。
(B)After the authentication server is confirmed, it is correct,Provide access to the client。
Client type#
according to OAuth 2.0 specification,Applications can be divided into confidential or public。The main difference is whether the application can hold the credentials safely(For example client ID and secret)。This will affect the type verification type that the application can use。
- confidential(confidential)
- public(public)
confidential(confidential)#
Confidential applications can save secret in a safe way,Will not expose it to unauthorized。They need a trusted back -end server to store Secret。You can use HS256 encryption and RS256 encryption
public(public)#
Public applications cannot safely hold Secret,Can only use RS256 encryption。
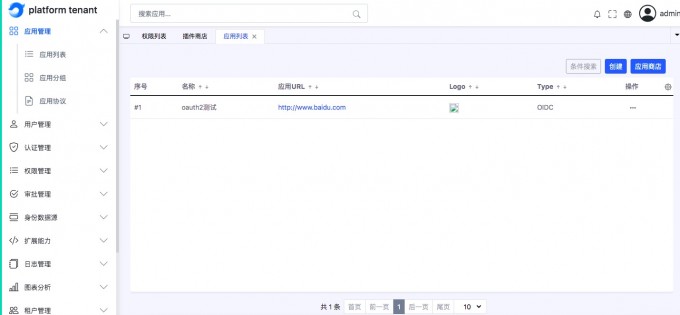
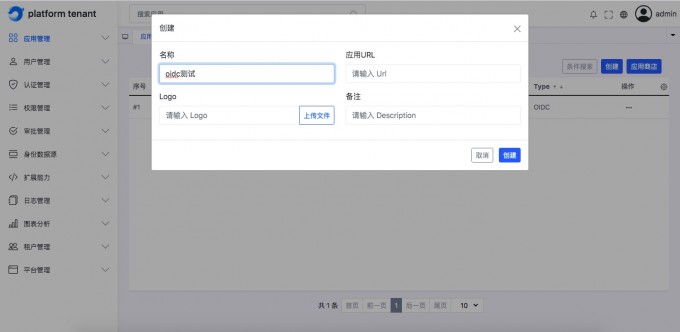
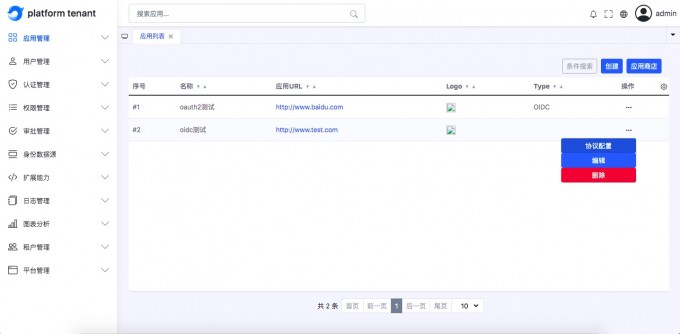
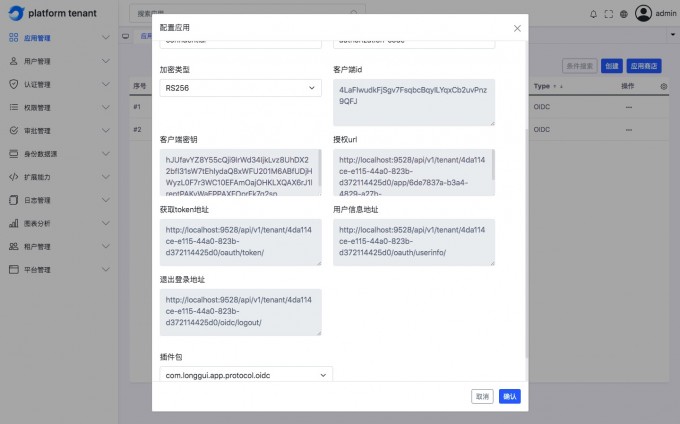
Add OIDC application#
How to hide the license page#
If the hidden authorization page switch is turned on,It will not allow users to choose whether to authorize,The user has logged in and directly authorized successfully,Enter the redirection page provided

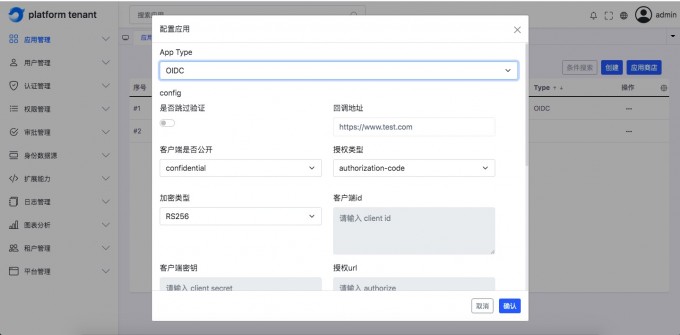
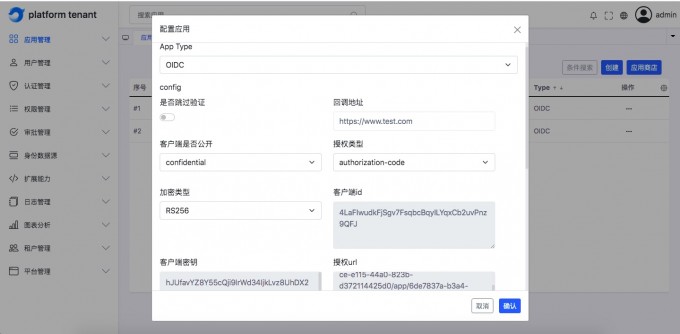
OIDC application#
-
Understand the meaning of the page field field#
English parameter name Corresponding page surface field redirect urlCallback address client_idClient ID client_tokenClient key authorize urlAuthorized URL get token urlGet ACCESS_Token address userinfo urlUser information address logout urlExit login address -
Get Authorization Code#
- Request address:
authorize url - Way of requesting: GET(Redirect)
- Request parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary client_idclient_idredirect_uriredirect urlresponse_typeFill in Code code scopeOptional ( openid userinfo) If you pass openid,Get token more ID will_token - Request example: http://authorize url/?client_id=xxxxx&redirect_uri=xxxxx&response_type=code&scope=userinfo
- Return parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary codeAuthorization code - Return sample: http://redirect_uri?code=As a savings, the seventh seven&token=Sadaa 4840, and I will be 04 with a 4 -wing 1 bastard 1 b 176
- Request address:
-
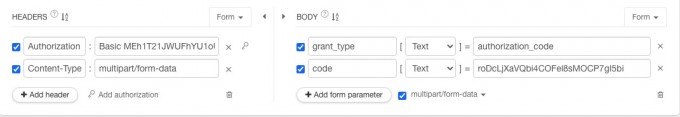
Get ACCESS Token#
- Request address:
get token url - Way of requesting: POST
- Request head parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary AuthorizationtokenFormat client_id:client_secret Use base64 encoding Basic Token Content-TypeFill in MULTIPART/form-data - Request parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary codeAuthorization code grant_typeFill in Authorization_code - Request example:
- Return parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary access_tokenToken expires_inExpiration token_typeBearer scopeuserinfo openid refresh_tokenToken to token - Return sample:
- Request address:
-
Get user information#
- Request address:
userinfo url - Way of requesting: GET
- Request head parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary AuthorizationBearer access_token Bearer cFcWq78HH9MKVQOFJgGPl6RFtESAc2 - Return parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary idUser ID nameuser name subUser ID sub_idUser ID preferred_usernameusername groupsUser group tenant_idTenant ID tenant_slugPractitioner Slug - Return sample:
- Request address:
-
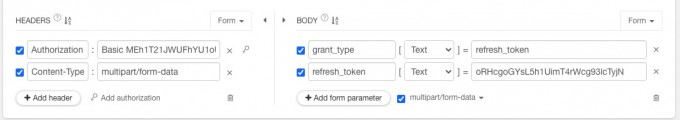
Refresh token#
This step is a option.,You can use this interface to replace the new token
- Request address:
get token url - Way of requesting: POST
- Request head parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary AuthorizationThis token is client_id and client_secret Basic Token Content-TypeFill in MULTIPART/form-data - Request parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary refresh_tokenUpdate token grant_typeFill in Refresh_token - Request example:
- Return parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary access_tokenToken expires_inExpiration token_typeBearer scopeuserinfo openid refresh_tokenToken to token - Return sample:
- Request address:
-
Exit OIDC#
This step is optional,You can exit user login,And jump to the specified address
- Request address:
logout url - Way of requesting: GET
- Request parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary id_token_hintid_token post_logout_redirect_uriThe address of the jump after the login (optional) - Return parameter:
parameter name Parameter Description Exemplary error_codeerror code error_msgError message - Return sample:
- Request address: